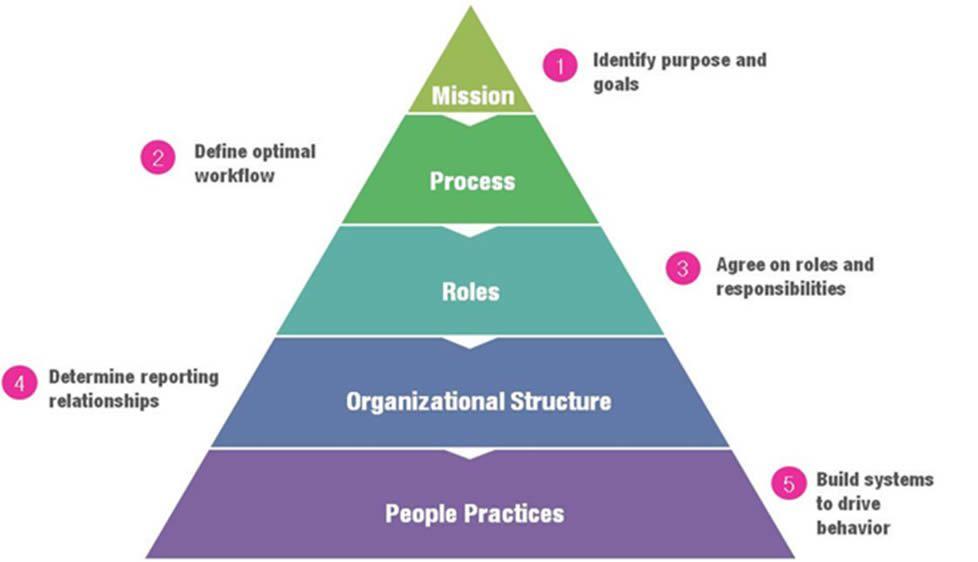
Introduction
A well-constituted body that is mutually established with a vow of loyalty to achieve a specific purpose or pre-determined goal is a formal organizational structure. It is characterized by a well-defined organizational structure, task specialization, division of work, and consistency of finished products, adhering to rules and regulations that are Implemented in addition to efficient communication networks. Thus, the formal organizational structure functions based on the operation of a well-structured and organized network that is both coordinated and well-managed by experts and Researchers in various areas of expertise. 1
In-Brief
- A network in which various cooperative ties are formed between different positions of organizations is a formal organizational structure that has been intentionally created for protecting Economic processes.
- The Decision-making task is made simple for individuals as a result of a formal organizational structure.
Keywords: Formal organizations, organizational structures, organizational designs, digital organizational model.
Formal Organizational Structures
Each individual is attached to various groups or clusters within an organization. Some of them are defined explicitly and more formally like organizational units, committees, departments, clubs, etc., whereas some groups are informal and they emerge from more vague and hidden factors like a community is connected due to their daily interactions or an alliance network. The formal organizational structure is a network that constitutes various cooperative ties between different positions in organizations that have been created intentionally for safeguarding economic processes. This study is mainly focused on the organizational structure, which is defined by the top management. The geographic structure is considered as an intentionally formed structure, and therefore, it is termed as formal. 3
Reasons for Formal Organizational Structure
1. The structure as an Empirical Object
This structure, rather macroscopic and theoretical, it is important for organizational communication mainly for two reasons. First, most of the characters or dimensions that are analyzed by the experts describe particularly Weber’s stipulation of written messages, communication processes, and upright discussion about exceptional problems. Second, an organization, which is an information-processing entity, forms the basis of many of these discussions.
2. The structure as an Information Processing Tool
The task of the decision-making process is eased for individuals by the formation of organizational structure, in addition to many other formalized organizational practices. Information about organizational structure informs the employee about what has to be done, whose orders to be followed, and whom to update about the employee’s activities and outcomes. The formal structure is designed in such a way that everyone has to do all tasks required by the organization, and that employees are enclosed by proper Information Environment to make appropriate decisions. Organizational structure varies according to the needs of an organization.
3. The structure as System Form
Organizational Structure isolates and restricts the limits of subunits. It also paves the way for their integrative coordination. To be brief, the organizational structure is used to determine the arrangement or the form of the system’s subunits significantly. Systems theory serves both as an analytical instrument which helps to stimulate attention towards new features of organizations and also forms the basis for the integration of the assets of other literature.
4. Structure as Negotiated
Decision making of organizations often quits from the state of wisdom. Members of an organization often have restricted resources of attention, and, in the vague, intricate situations, attention can be paid to part of decisions and by formal criteria, other issues should concern them. When ambiguity and complexity of organizations are distinctive, participants, problems, solutions, and choice opportunities are badly built in a random way.
5. The structure as Carrier of Social Psychological Processes
The organizational structure serves as a stimulus to other phenomena. Due to the formal structure of organizations, its socio-psychological processes have been transformed. 2
An organizational structure that supports digital transformation
Digital Technologies assist organizations to reinvent the whole process of business and also to establish new ones. Some experts realized the effectiveness of the use of an organizational structure which has been characterized by decentralized decision-making, more flattening structure, rapid transfer of knowledge among employees, greater coordination and collaboration, team working, knowledge networking, parallel communication, practical approach, agility, and flexibility. As old technical models were not flexible, with strong internal and external boundaries, the progress of the new structure of the organization is unavoidable. Old models lack the potential to respond rapidly to changes in a hyper-connected environment. 4
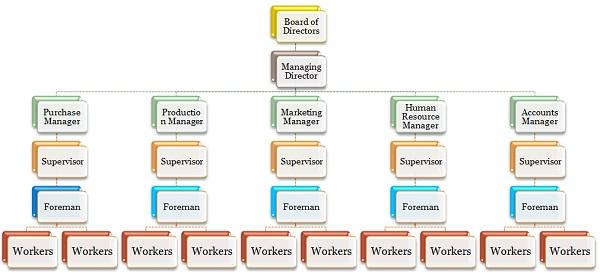
Features of Formal organization:
(1) The process of organizing has intentionally created a formal organizational structure.
(2) The achievement of the goal of organizations is the purpose of the formal organization structure.
(3) Each individual has got a specific task in the formal structure of organizations.
(4) Each individual has decision-making power in the formal organizational structure.
(5) The superior-subordinate relationship has been formed in the formal organizational structure.
(6) A scalar chain of communication has been formed in the formal organizational structure.
Advantages of Formal Organizational Structure
1. Systematic Working: Organization has got systematic and smooth functioning due to the formal organizational structure.
2. Achievement of Organizational Objectives: Organizational objectives have been established by the formal organizational structure.
3. No Overlapping of Work: Every departments and employee have work divided among them in the formal organizational structure. So overlapping or duplication of work can always be avoided.
4. Co-ordination: Activities of various departments have been coordinated as a result of formal organizational structure.
5. Creation of Chain of Command: superior-subordinate relationship has been well-established in the formal organizational structure.
6. More Emphasis on Work: importance is given to work than interpersonal relations in the formal organizational structure.
Disadvantages of Formal Organization
1. Delay in Action: Actions may get delayed while following the chain of order and scalar chain.
2. Ignores Social Needs of Employees: Social and psychological needs of employees were not given importance in the formal organizational structure which leads to a lack of motivation among employees.
3. Stresses on Work Only: Work is given more importance in the formal organizational structure. Human relations, talents, and creativity were ignored. 5
Conclusion
Formal structures mean purposely designed organizations that result from larger institutional arrangements. Research carries in various disciplines recommends that formal organizational structure can form beliefs, opinions, and behaviors of individuals. In the literature of organizational theory, formal organizations are illustrated as the opinions and characteristics of organizational members that have been restricted by shared organizational culture. 6 It is proved that the process of informal organization has not generally been damaging to the development and growth of the formal organization.
Future scope
Researchers better understand the consequences of formal organizational structures on the apparent strategic alignment. Organizations should look for the lateral mechanisms to break the impact of silos due to significance over the influence of the functional division. Future research should be carried out to identify a mechanism that reveals the insights on the alignments that progress in companies. It could be both beneficial to both experts and scholars to identify the evolution of insights in the context of the structural changes by conducting a study.
References
- Comfort R. Etor, 2019, Formal and informal organizations.
- Robert D. McPhee, 2018, Formal Structure and Organizational Communication.
- P. Lahdelma, The Effect of Formal and Informal IntraOrganizational Structures on the Perceived Strategic IT-Business Alignment.
- Vladimir Mirković, Jelena Lukić, Snežana Lazarević, Željko Vojinović, 2019, Key Characteristics Of Organizational Structure That Supports Digital Transformation, Strategic Management and Decision Support Systems in Strategic Management
- Therence Apostol, 2019, The formal and informal organization structure.
- Christina Prell, Mark Reed, Liat Racin, Klaus Hubacek, 2019, Competing Structure, Competing Views: The Role of Formal and Informal Social Structures in Shaping Stakeholder Perceptions
- Guidelines to Write a Research Proposal for Neurology Research Scholars - March 19, 2021
- How to Choose a PhD Dissertation Topic For Economic Research? List out the Criteria for Topic Selection - March 11, 2021
- Beginners Guide to Write a Research Proposal for a PhD in Computer Science - February 19, 2021
