BUSINESS AND MANAGEMENT
Marketing
Application of Augmented Reality for boosting Experiential Marketing Initiatives and Enhancing Outcomes
Sep 20, 2019
In brief
- This article briefly presents a look into the tremendous potential of augmented reality in the domain of experiential marketing.
- The article also highlights how augmented reality is being used in diverse industry sectors to increase sales and achieve organizational objectives.
Marketing as a concept and practice has existed for a long time now. It can be said that from the time people started trading, marketing became an integral part of trade. Nonetheless, the process of marketing has experienced an evolution over time. In recent times, marketing has shifted from conventional to contemporary which presented several advantages to marketers. Marketing in its contemporary form is continuously evolving with technological developments. Digitization and the introduction of smartphones have upped the game further. All such alterations focus on enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of marketing. Of late, marketers have been attracted to and are being lured to deploy augmented reality in their marketing strategies. Augmented reality has gained much prominence in recent times and is being extensively used.
Augmented Reality
In layman’s terms, augmented reality (AR) is a technology that enables the placement of virtual objects in the real world, in real-time, thereby enhancing the customer’s knowledge about the world around. Augmented reality is largely utilized in tandem with apps on smartphones to enhance the real world by merging digital elements within it, but still being in a position to tell them apart. Augmented reality is very different from technologies that have been in existence in the past. While AR is being utilized to cater to similar marketing initiatives, building an experience using AR as medium needs to be approached with a fundamental knowledge of the manner in which it blends with the wider business objectives. AR adds a digital overlay to the actual environment that exists and it has already transformed the way in which people shop, try new products prior to making a purchase and engage with brands. A popular example of AR in marketing refers to the mobile app ‘Pokemon Go’ where users caught virtual creatures which were projected into the actual world when viewed through a smartphone.

Figure 1: Augmented Reality – Pokemon Go
Augmented Reality in Marketing
In simple terms, organizations adopt an array of marketing strategies to understand a product or service value and later convey this information to customers to ensure increased sales. However, it is imperative that the marketer is aware as to what will be served and the intended audience could then follow the campaign to meet their needs while marketers can be sure of long term loyalty. A common form of AR that is used with video in the current day is the superimposed 10-yard line during NFL broadcasts. What makes AR so successful is the fact that audiences are seldom aware that it is AR as it is seamlessly integrated within the broadcast experience and offers value for the broadcast viewer. Utilizing AR in marketing is apparently not very expensive as compared to traditional marketing strategies. Marketing campaigns and advertisements that are print based are comparatively very expensive and warrant the need for consistent investments in terms of resources. Whereas, AR as a technology that is based on computers is relatively cheap as it can be applied online or on digital platforms. While the cost of development in terms of establishing AR based marketing campaigns could be higher, costs pertaining to lifetime operations would remain the same. This claim is substantiated through the statement made by Vivian Rosenthal, Founder and CEO of Goldrun;
“It honestly depends on the scope of the project, but AR campaigns can be as inexpensive as $5000 and as high as $100,000. That is nothing compared to print, and in many ways it’s worth the risk in my eyes”
As of now, AR is being effectively utilized for marketing in several industry sectors though not extensively but scantly, with impressive outcomes.
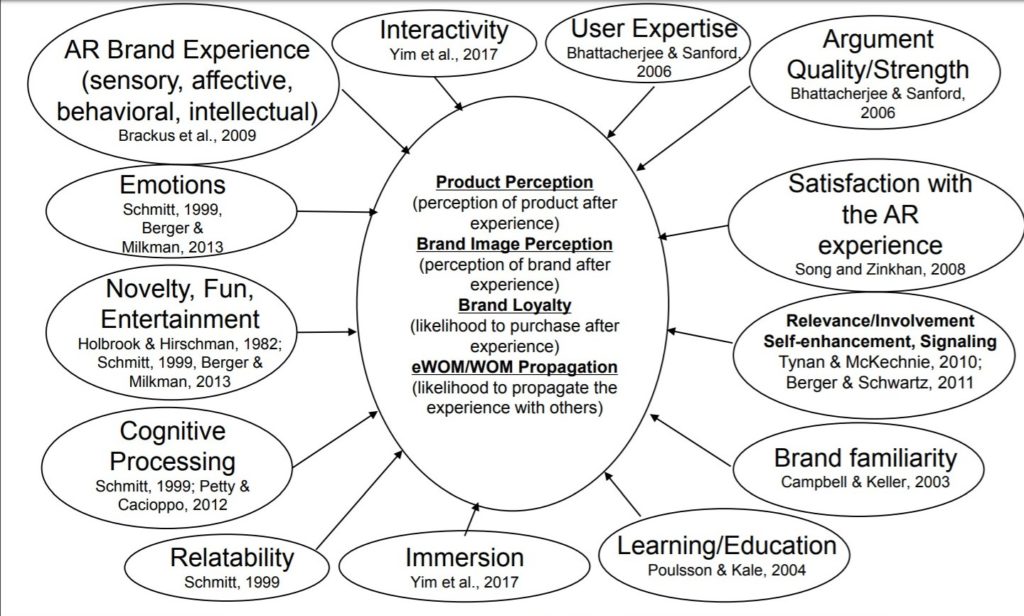
Brands that Implemented AR
- IKEA
- NIKE
- AMERICAN APPAREL
- TOPSHOP & AMAZON
- MINI
- ADDIDAS
Brands that Implemented AR
The popularity of AR in the real estate sector is increasing and realtors are gaining much interest in the concept. Realtors have realized that potential buyers can be engaged through visual interaction. With AR, buyers are in a position to merge themselves with the property on sale. On the basis of 2D blue print, an AR app can generate a 3D image of the proposed property (even before construction has started) that can be viewed from diverse angles. Buyer can also dismantle sections of house to view and understand the layout of various floors. Using an AR app on their smartphones, buyers can create a window into the property, enabling them to take a virtual tour of the property. Buyers can also point their AR enables smartphones to point at a property on sale and get information pertaining to its price, specifications and owner’s contact details..

Figure 2: From 2D to 3D

Museum Marketing via AR
Museums are now using AR marketing as a strategy to interpose a real world with a virtual world which offers visitors with a dynamic view and understanding about the origins, details and history of the many artifacts and exhibits on display.
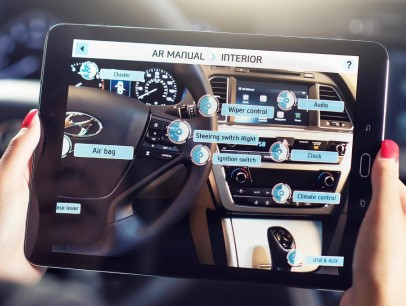
Automobile Marketing via AR
Heavy investment is involved in purchase of a car therefore customers, before arriving at a purchase decision need to be thoroughly convinced. It is the job of the marketer to convince the customer to make a purchase decision. Automobile marketers with the help of AR are now able to provide tools and means to customers using which they can compare their options. As a result, automobile manufacturers are resorting to AR to market their products. In recent times, Volvo marketed their S60 model car by developing an AR experience on YouTube. This enabled potential customers to drive a virtual car by simple left and right movement of their smartphones. This led to a 293% increase in traffic to their YouTube channel and eventually leading to increased sales.
Future Scope
This particular article focused just on a singular aspect ‘marketing’ whereas, it did not touch upon other facets such as ‘branding, consumer behaviour’, etc. Even in research circles, more emphasis has been on addressing the ‘marketing’ aspect and not much research has been conducted on the other interlinked aspects of marketing from the perspective of AR.
- Researchers can further refer Javornik’s (2016) augmented reality research agenda, as well as Rese et al (2017), Kim and Hyun (2016) and Yim et al (2017) research on the adoption of AR mobile apps.
- Research in this domain in future could revolve around investigating other techniques through which AR can be utilized to influence brand perceptions.
- Research needs to be carried out to understand how AR can be utilized effectively to conveying brand stories.
- Considering the tremendous potential of AR, the use of AR for various applications in healthcare sector needs to be investigated, to understand how AR can enhance health outcomes.
- Tapscott. D, (2014), “The Digital Economy Anniversary Edition: Rethinking Promise and Peril in the Age of Networked Intelligence”, McGraw-Hill Education; 2 edition, ISBN-13: 978-0071835558.
- W.H. Drath et al., (2008), “Direction, alignment, commitment: Toward a more integrative ontology of leadership”, The Leadership Quarterly, Vol. 19, pp. 635–653.
- David J. Deming, (2017), “The Growing Importance Of Social Skills In The Labor Market”.
- F.J. Yammarino et al, (2012), “Collectivistic Leadership Approaches: Putting the ‘‘we’’ in Leadership Science and Practice”, Industrial and Organizational Psychology, Vol. 5, 382–402.
- Farazmand. A (ed.), (2016), “Relational Leadership Theory”, Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance
- Smith, A. M., & Green, M., (2018), “Artificial Intelligence and the role Of Leadership”, Journal Of Leadership Studies.
- Sun Z., (2018), “Artificial Leadership: An Artificial Intelligence Approach”, Artificial Leadership. PNG UoT BAIS, Vol. 3, Issue 12, pp. 1-7.
- Sun. Z., “A Framework for Developing Management Intelligent Systems”, International Journal of Systems and Service-Oriented Engineering, Vol. 6, Issue 1, pp. 37 – 53.
- Brynjolfsson. E , (2016), “The Second Machine Age – Work, Progress, and Prosperity in a Time of Brilliant Technologies”, W. W. Norton & Company; Reprint edition, ISBN-13: 978-0393350647.
- How to develop mathematical theorems based on literature survey for PhD thesis? - December 28, 2020
- How big data analytics interacts with digital forensics. Mention the challenges, impacts and forensic solutions in it for writing a research proposal - November 24, 2020
- Explain the factors affecting the choice of title for PhD dissertation? - August 29, 2020

